The dumbbell bench press is a classic and highly effective exercise that targets the chest, shoulders, and triceps while also engaging the core for stability. It offers an excellent alternative to the traditional barbell bench press, allowing for a greater range of motion, muscle activation, and reduced risk of injury. Whether you’re a seasoned gym-goer or a fitness enthusiast just starting out, incorporating the bench press into your workout routine can bring remarkable strength and muscle gains. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of the dumbbell bench press, its benefits, proper technique, and various training methods to maximize its potential.
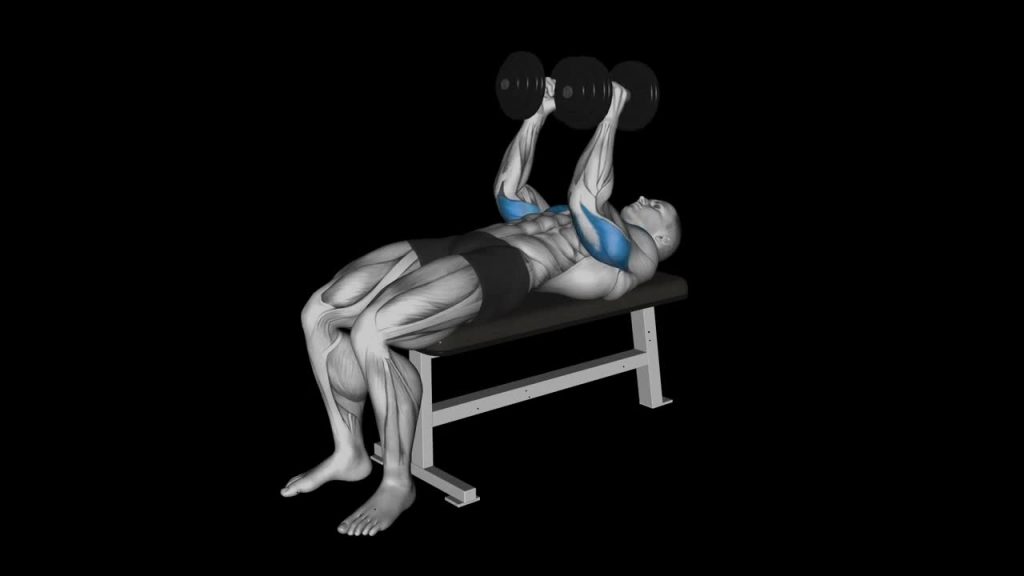
Benefits of the Dumbbell Bench Press:
Greater Range of Motion:
One of the primary advantages of the dumbbell bench press is that each arm works independently. This leads to a greater range of motion, allowing you to work through a fuller stretch at the bottom of the movement. The increased range stimulates muscle fibers more effectively, contributing to muscle growth and overall strength gains.
Improved Muscle Balance:
The unilateral nature of the exercise helps identify and address muscle imbalances between the left and right sides of the body. By using dumbbells, you can prevent one dominant arm from compensating for the weaker one, promoting symmetry and balance in the upper body.
Engages Stabilizer Muscles:
Unlike the barbell bench press, which relies on a stable bar, the dumbbell bench press requires the use of stabilizer muscles to control and balance the weights independently. This leads to improved functional strength and helps prevent injuries during everyday activities.
Joint-Friendly:
Dumbbells offer a more natural and joint-friendly movement pattern compared to barbells. This can be beneficial for individuals with shoulder issues or other mobility limitations, as it reduces stress on the shoulder joints.
Proper Technique for the Dumbbell Bench Press:
Set-Up:
Begin by selecting a pair of dumbbells of an appropriate weight for your fitness level. Sit on a flat bench with your feet firmly planted on the ground. Position the dumbbells on your thighs, then lie back on the bench, keeping your back flat and shoulders pulled back. Ensure your feet, hips, shoulders, and head are in contact with the bench throughout the exercise.
Grip:
Grasp the dumbbells with an overhand grip, keeping your palms facing forward. Position the dumbbells directly above your shoulders, so your arms are perpendicular to the floor.
Lowering Phase:
Inhale and slowly lower the dumbbells towards the sides of your chest in a controlled manner. Maintain a slight arch in your lower back and keep your elbows at a 45-degree angle to your body.
Pressing Phase:
Exhale and push the dumbbells back up to the starting position while squeezing your chest muscles. Keep your wrists aligned with your elbows and avoid locking your elbows at the top of the movement.
Repeat:
Complete the desired number of repetitions while maintaining proper form and control throughout the exercise.
Variations of the Dumbbell Bench Press:
Incline Bench Press:
Adjust the bench to an inclined position (around 30-45 degrees) to target the upper chest more intensely.
Decline Bench Press:
Adjust the bench to a declined position (around 15-30 degrees) to emphasize the lower chest and engage the lower pectoral muscles.
Neutral Grip Bench Press:
Use dumbbells with neutral grips (palms facing each other) to reduce strain on the wrists and engage the triceps more effectively.
Single-Arm Bench Press:
Perform the bench press with one arm at a time to increase the challenge of stability and core engagement.
Training Methods for Dumbbell Bench Press:
Strength Training:
To build strength, perform 3-5 sets of 4-6 repetitions using heavier weights. Rest for 2-3 minutes between sets to allow for sufficient recovery.
Hypertrophy Training:
For muscle growth, perform 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions with moderate weights. Rest for 60-90 seconds between sets.
Endurance Training:
To improve muscular endurance, perform 2-3 sets of 15-20 repetitions with lighter weights. Shorten the rest periods to 30-45 seconds.
Incorporating Dumbbell Bench Press into Your Routine:
The dumbbell bench press can be included in your upper body or push day workout routine. Here’s a sample upper body workout incorporating the dumbbell bench press.
Dumbbell Bench Press: 4 sets x 8 reps
Bent-Over Dumbbell Rows: 3 sets x 10 reps
Dumbbell Shoulder Press: 3 sets x 10 reps
Dumbbell Bicep Curls: 3 sets x 12 reps
Tricep Dips: 3 sets x 12 reps
Plank: 3 sets x 30-60 seconds
Effective Exercise:
The dumbbell bench press is a versatile and effective exercise that should be a staple in any comprehensive strength training program. Its numerous benefits, such as increased range of motion, muscle balance, and engagement of stabilizer muscles, make it an invaluable addition to your fitness routine. By mastering proper technique and incorporating different variations and training methods, you can maximize the potential of the dumbbell bench press and unlock significant strength and muscle gains. Remember always to listen to your body, progress gradually, and consult a fitness professional if you’re unsure about any aspect of your training. Now, go ahead and embrace the challenge of the dumbbell bench press to sculpt a stronger and more well-rounded physique.
•For More Interest Best Adjustable Kettlebell Set
•For More Information Click Here




One thought on “Dumbbell Bench Press”